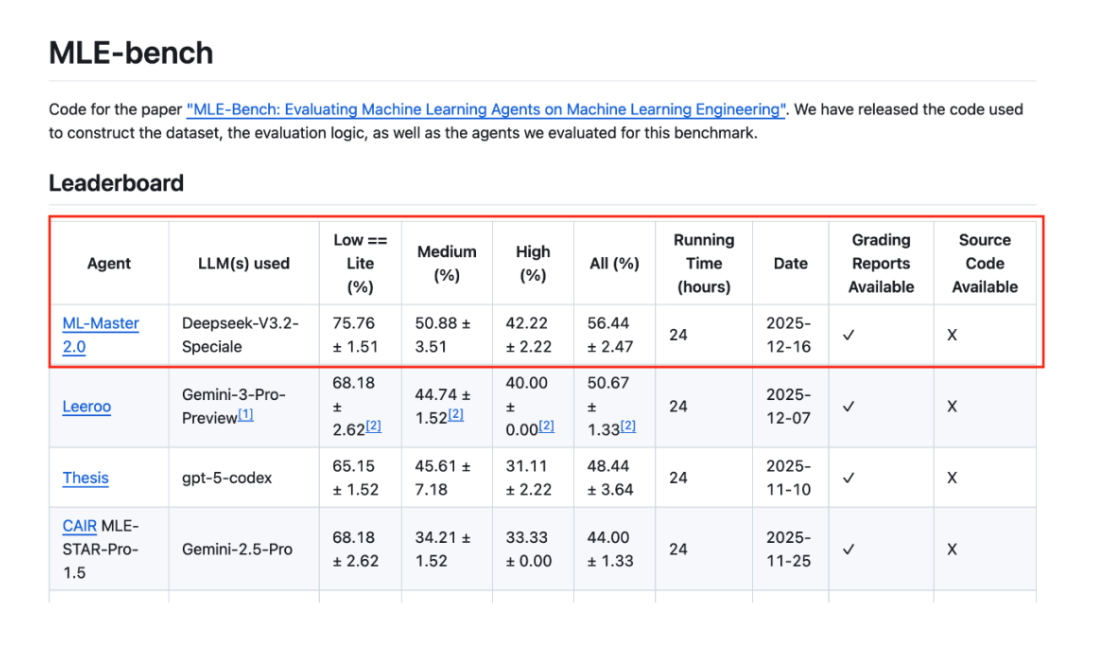
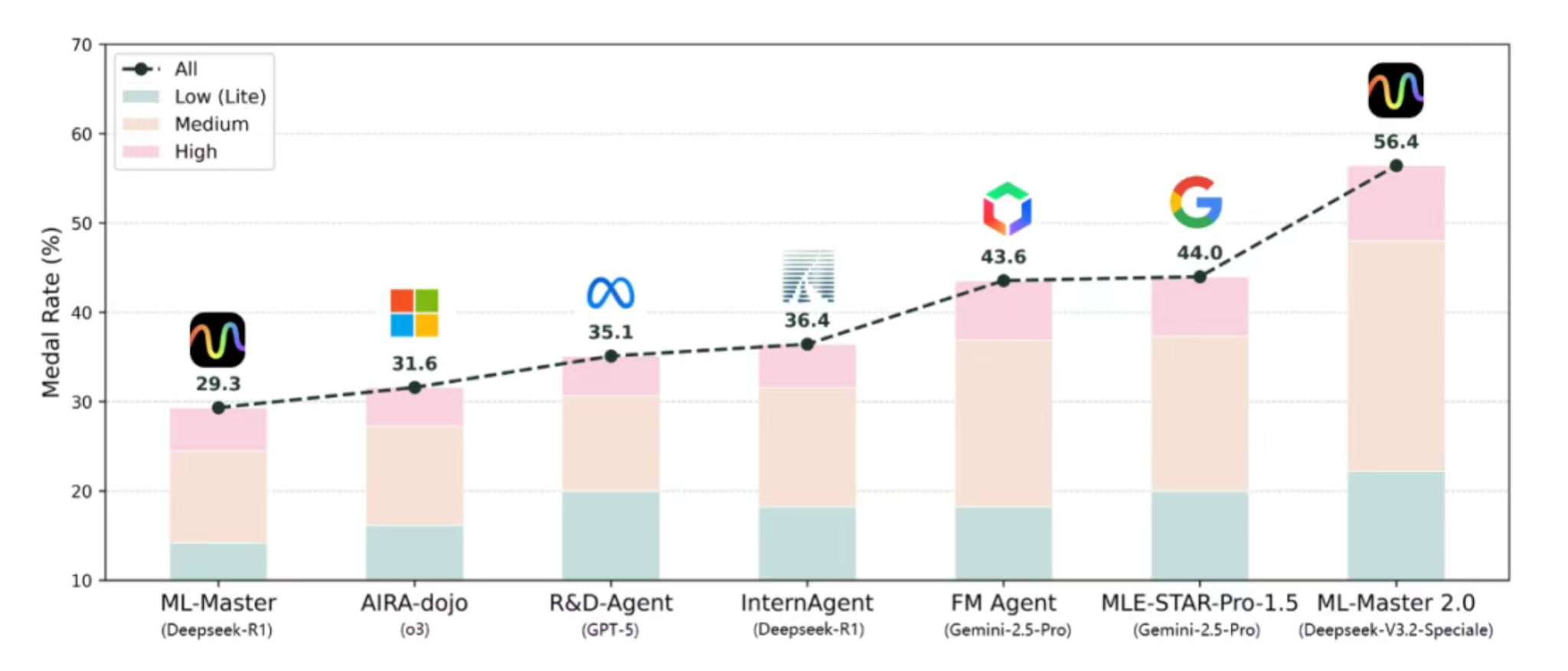
The SciMaster & Eigen AI team has officially unveiled ML-Master 2.0, an autonomous AI agent for machine learning engineering. Powered by the open-source DeepSeek model, the agent has achieved a new State-of-the-Art (SOTA) on OpenAI’s MLE-bench, surpassing established benchmarks from Google, Meta, and Microsoft. The system is now opening its waiting list on the SciMaster platform for researchers worldwide.
From Science Fiction to Reality
Humanity has long envisioned agents capable of autonomous exploration—from the “Sophons” in The Three-Body Problem interfering with fundamental physics, to “HAL” in 2001: A Space Odyssey, and Asimov’s reasoning robots. The core question remains:
What happens when intelligent agents evolve from mere tools into autonomous engineers capable of long-term hypothesis testing and self-correction?
As Large Language Model (LLM) capabilities advance, this is moving from imagination to a technical imperative. Researchers now recognize that the true milestone is not whether an AI can “solve a puzzle,” but whether it can distill signals out of noise in iteratively finding the “optimal solutions” in long-term research.
- Google DeepMind’s AlphaEvolve seeks to refine strategies through long-term evolution.
- OpenAI’s Frontier Science focuses on iterative performance in real scientific tasks.
- The Genesis Mission (often referred to as the “AI Manhattan Project”) aims to integrate AI into national-level scientific frameworks systematically.
These diverse paths converge on a single consensus: The AI that truly drives progress must withstand long-term trial and error in real research environments. This has accelerated the AI4AI (AI for AI) movement, where the focus is on AI driving its own growth to support increasingly complex scientific tasks.
The Challenge of Machine Learning Engineering (MLE)
OpenAI’s MLE-bench targets Machine Learning Engineering (MLE) precisely because it mirrors the reality of research. Unlike idealized Q&A, real MLE involves cycles of experimental design, coding, debugging, and analysis that can last dozens of hours. This makes MLE-bench one of the few benchmarks capable of reflecting an AI’s capacity for long-term scientific evolution.
ML-Master 2.0, developed by a joint team from the School of Artificial Intelligence at Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU), the Shanghai Institute for Algorithms and Innovation, and DP Technology, was built specifically for this mission. Supported by EigenAI’s high-performance infrastructure and built on the DeepSeek-V3.2-Speciale open-source model, the agent achieved the global #1 spot on MLE-bench, outperforming agents developed by teams at Google, Meta, and Microsoft.
More importantly, ML-Master 2.0 is already being utilized in laboratories for frontier applications, including Embodied AI training and Theoretical Physics simulations.
Architecture: Built for Ultra-Long-Horizon Autonomy
Real-world research is rarely about getting it right on the first try; it is a cycle of hypothesis, failure, and revision. ML-Master 2.0 is designed around Ultra-Long-Horizon Autonomy, emphasizing three key capabilities:
- Persistence: Staying aligned with a research goal for over 10+ hours of operation.
- Learning from Failure: Extracting patterns from unsuccessful experiments rather than repeating mistakes.
- Knowledge Transfer: Moving acquired insights from one task to the next.
Hierarchical Cognitive Caching (HCC)
To manage these long-term tasks without “context explosion,” ML-Master 2.0 introduces Hierarchical Cognitive Caching (HCC). This treats context as a living asset rather than disposable data:
- Experience: Immediate execution paths for current decisions.
- Knowledge: Stable conclusions verified through repeated testing.
- Wisdom: High-level strategies and cognitive prototypes are reusable across different tasks.
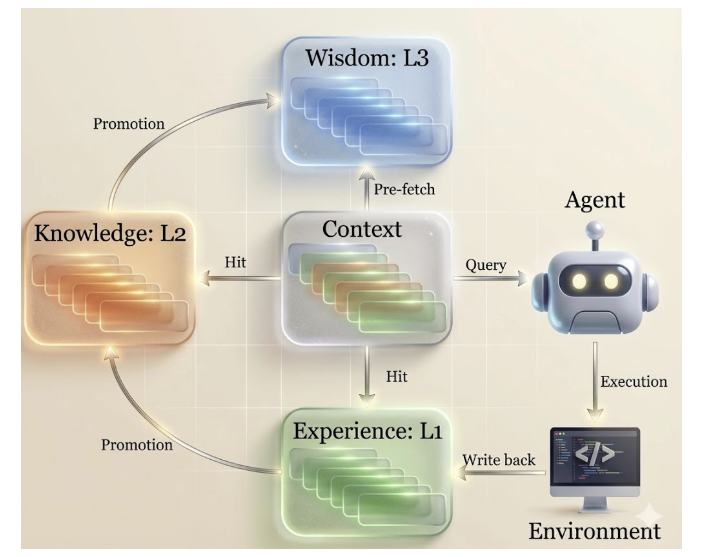
By filtering and promoting valuable insights through these layers, the system maintains a stable research rhythm, effectively managing the “memory” of the scientific process.
Conclusion: The Era of the autonomous AI Engineers
The results on MLE-bench—a 56.44% medal rate, marking a 28.3% improvement over previous leading models—demonstrate that treating cognitive processes as evolvable resources is the key to autonomous discovery.
The core code for ML-Master is currently open-sourced on GitHub.
- Project GitHub: https://github.com/sjtu-sai-agents/ML-Master
- EigenAI: https://www.eigenai.com/
